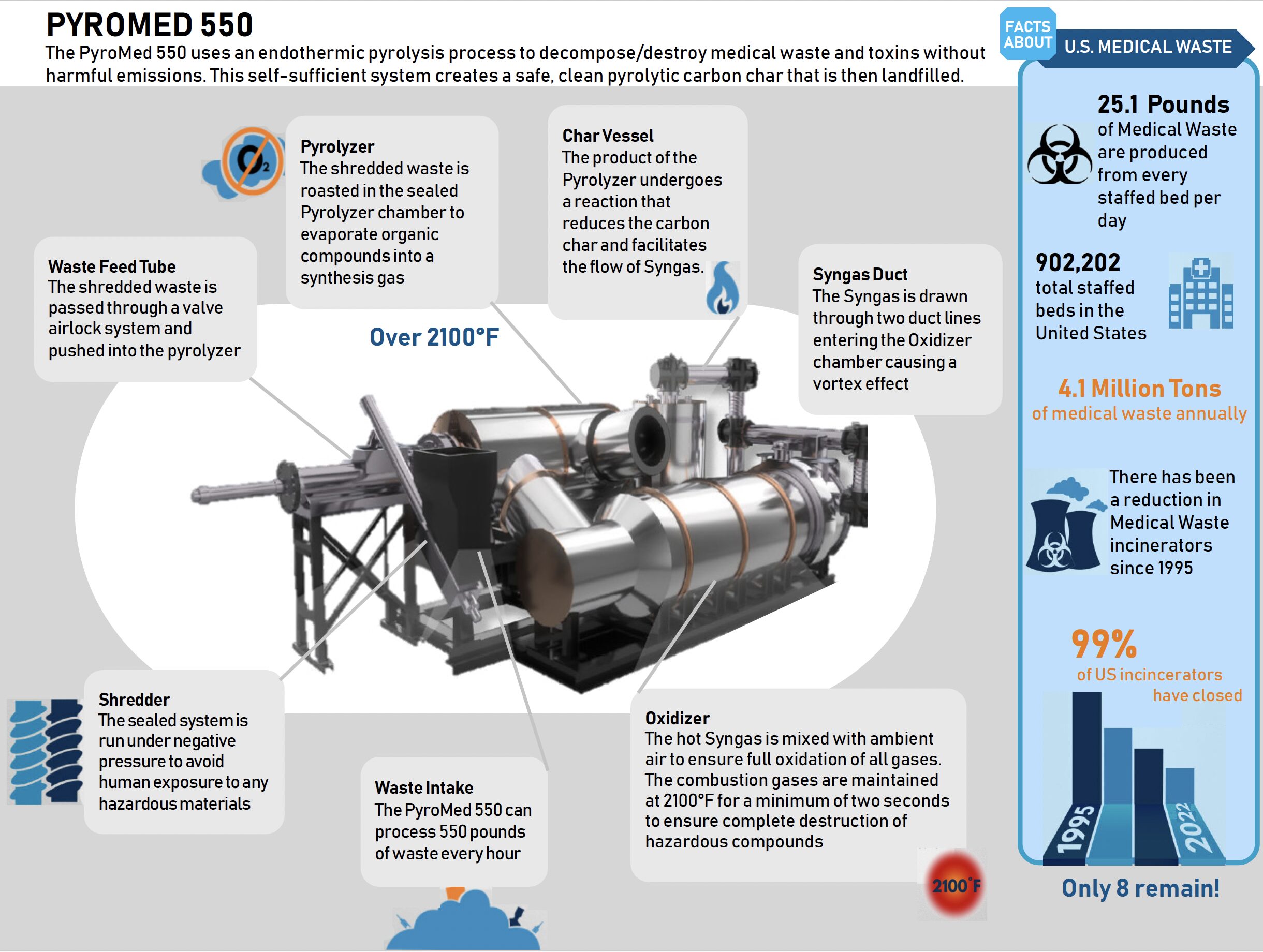
In early 2010, we recognized an enormous and rapidly growing need for an innovative solution to address the challenges of waste destruction.
Since 1995, more than 99% of the medical waste incinerators in the US have been closed.
The trend was obvious.
The need for an environmentally safe technology for the destruction of medical waste had become a mandate across the country.
We have the solution.
After researching methods and other critical factors we identified a compact, small-scale, proven technology to create an environmentally-friendly replacement for incineration. Since then, we have painstakingly designed a system specific to medical waste and own all intellectual property, trade secrets, and know-how to the PyroMed™ pyrolysis technology to address all regulated and hazardous wastes in the U.S. and internationally.
Waste Receiving and Conditioning.
Arriving waste is weighed and directed to an enclosed, secure location within the building. Following initial inspections and documentation, the waste is staged in a controlled manner and prepared for the final destruction process.
Pyrolysis
Pyrolysis is defined as the decomposition of material using an external, indirect heat in an oxygen-free environment. Utilizing moderately low temperatures, the waste slowly roasts as it absorbs the heat and decomposes within a sealed airless chamber which is classified as an endothermic process. Volatile organic compounds boil-off in the form of synthesis gas which is later oxidized in a controlled manner. Because waste material is not directly subjected to elevated temperatures and combustion gases exceeding 900◦C, harmful emissions, such as dioxins and furans, are simply not able to form. This unique distinction prompted the federal EPA to grant a special exemption for Pyrolysis as outlined within 40 CFR 60 and 62 rulings regarding incineration of hazardous, infectious waste, and medical waste.
Renewable Energy (Heat) Generation.
The system produces heat that can be leveraged to create steam and offset the use of fossil fuels. The steam can also be converted directly to electricity by incorporating a turbine genset.